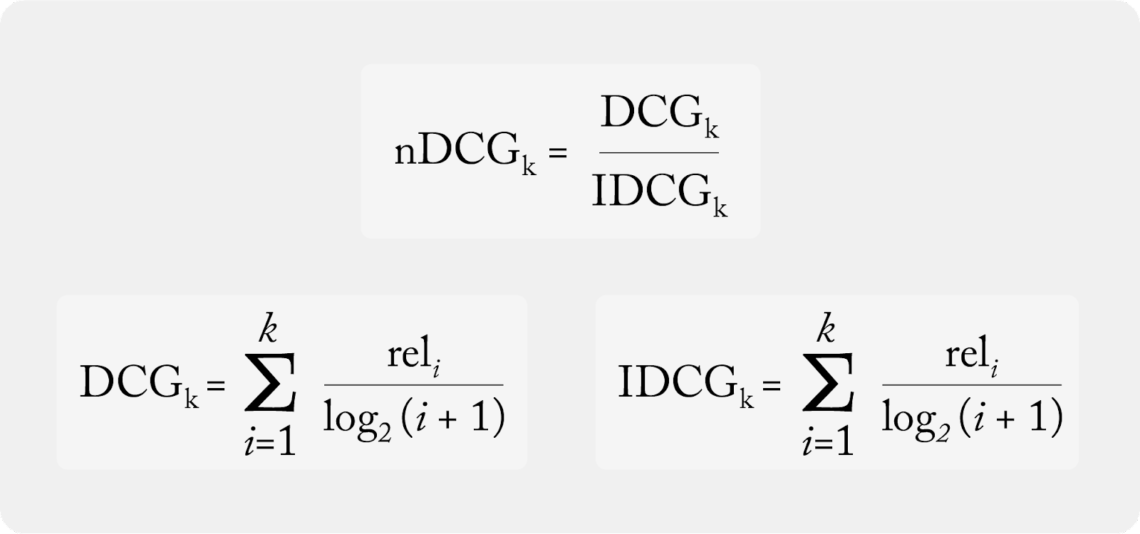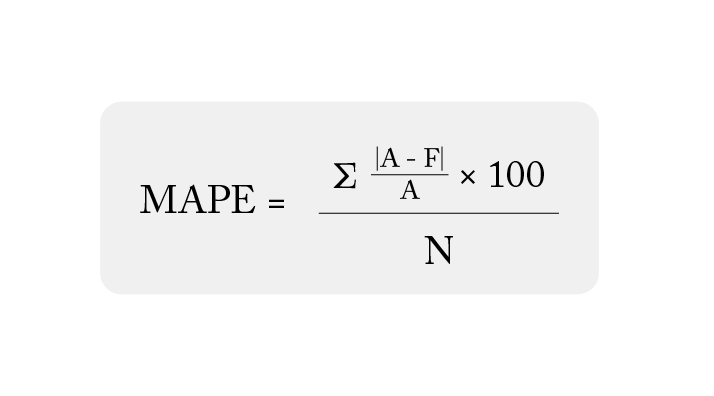Latest Posts
-
·
Understanding LLM | A Transformative Reading List
Large language models have taken the public attention by storm – no pun intended. In just half a decade large language models – transformers – have almost completely changed the field of natural language processing. Moreover, they have also begun to revolutionize fields such as computer vision and computational biology. The following list below is…
-
·
Kolmogorov Smirnov Test: When and Where To Use It
What is the Kolmogorov-Smirnov Test (KS test or K-S test)? The Kolmogorov Smirnov test (KS test or K-S test) is used to compare two distributions to determine if they are pulling from the same underlying distribution. In the typical ML use case, there are two distributions (A & B) that you are trying to compare.…
-
·
Jensen Shannon Divergence: Intuition and Practical Application
What Is JS Divergence (JS Div)? The Jensen-Shannon divergence (JS) metric – also known as information radius ( IRad ) or total divergence to the average – is a statistical measurement with a basis in information theory that is closely related to Kullback-Leibler divergence (KL Divergence) and population stability index (PSI) . The advantage of…
-
·
KL Divergence: When To Use Kullback-Leibler divergence
The basics of KL divergence and how it is used in drift monitoring What Is KL Divergence? Kullback-Leibler divergence metric is a statistical measure from information theory that quantifies the difference between one probability distribution from a reference probability distribution. KL divergence is also known as relative entropy. This post covers: KL Divergence Formula KL…
-
·
Population Stability Index (PSI): What You Need To Know
Population stability index (PSI) is a statistical measure with a basis in information theory that quantifies the difference between one probability distribution from a reference probability distribution. The advantage of PSI over KL divergence is that it is a symmetric metric. PSI can be thought of as the round trip loss of entropy – the…
-
·
Monitoring Text-Based Generative AI Models
Tips for measuring text-based generative models using BLEU, ROUGE, METEOR, and Bertscore as well as prediction embeddings In recent years, text-based generative AI models have been making significant strides in natural language processing tasks such as language translation, text summarization, and dialogue generation. These models are capable of generating text that is often indistinguishable from…
-
·
Normalized Discounted Cumulative Gain (NDCG)
Overview Ranking models underpin many aspects of modern digital life, from search results to music recommendations. Anyone who has built a recommendation system understands the many challenges that come from developing and evaluating ranking models to serve their customers. While these challenges start from the data preparation and model training and continue through model development…
-
·
R Squared: Understanding the Coefficient of Determination
Introduction The R-squared metric — R², or the coefficient of determination – is an important tool in the world of machine learning. It is used to measure how well a model fits data, and how well it can predict future outcomes. Simply put, it tells you how much of the variation in your data can…
-
·
Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE): What You Need To Know
What Is Mean Absolute Percentage Error? One of the most common metrics of model prediction accuracy, mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) is the percentage equivalent of mean absolute error (MAE). Mean absolute percentage error measures the average magnitude of error produced by a model, or how far off predictions are on average. While understanding this…